Blogs by Manglam Chemicals
The Essential Role of Manganese: Exploring its Importance and Applications in Chemistry
Introduction
Manganese, a versatile transition metal, plays a crucial role in various chemical processes. From its essential role in biological systems to its widespread industrial applications, manganese compounds exhibit a diverse range of properties and functionalities. This blog post will delve into the significance of manganese in chemistry, exploring its key applications and highlighting the importance of understanding its chemical behavior.
1. Biological Significance of Manganese
- Enzyme Cofactor: Manganese is an essential cofactor for numerous enzymes involved in vital biological processes. These enzymes catalyze reactions such as photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and antioxidant defense.
- Role in Bone Health: Manganese contributes to bone formation and maintenance by regulating the activity of enzymes involved in bone metabolism.
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Manganese plays a crucial role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are essential for proper brain function and communication.
2. Industrial Applications of Manganese Compounds
- Steel Production: Manganese is a key alloying element in steel production. Manganese compounds are added to steel to enhance its strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
- Pigments and Dyes: Manganese compounds are used to produce a variety of pigments and dyes, including brown, purple, and black pigments.
- Batteries: Manganese dioxide (MnO2) is a widely used cathode material in alkaline batteries, powering various electronic devices.
- Fertilizers: Manganese compounds are added to fertilizers to improve crop yields by providing essential nutrients to plants.
- Chemical Oxidants: Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a strong oxidizing agent used in various chemical reactions, including water treatment and organic synthesis.
3. Chemical Properties of Manganese Compounds
- Variable Oxidation States: Manganese exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, from -3 to +7, leading to diverse chemical properties and reactivities.
- Complex Formation: Manganese readily forms complexes with various ligands, including water, ammonia, and organic molecules.
- Catalytic Activity: Many manganese compounds exhibit catalytic activity, making them valuable in various industrial processes.
4. Environmental Considerations
- Manganese Pollution: Excessive manganese in the environment can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems.
- Waste Management: Proper waste management practices are crucial to prevent the release of manganese compounds into the environment.
Manganese compounds play a vital role in various aspects of our lives, from the biological processes within our bodies to the industrial processes that shape our modern world. Understanding the chemical properties and applications of manganese is crucial for developing new technologies, improving human health, and protecting the environment.
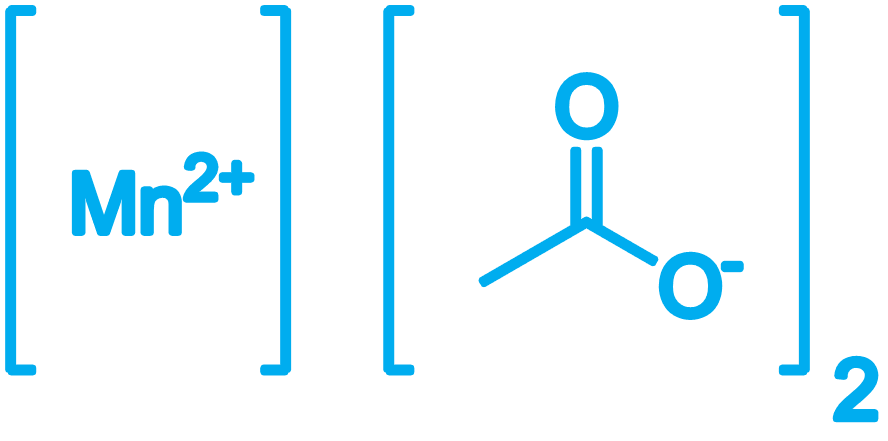
Manganese Acetate
CAS No: 6156-78-1
Manganese(II) acetate are chemical compounds with the formula Mn(CH3CO2)2.(H2O)n where n = 0, 2, 4.. It is used as a catalyst and as fertilizer.
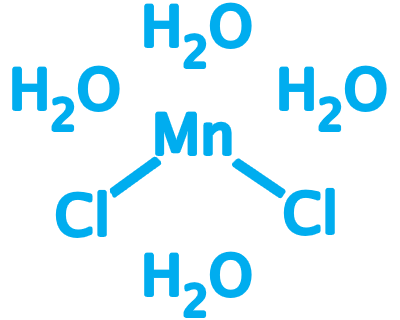
Manganese Chloride
CAS No: 13446-34-9
Manganese(II) chloride describes a series of compounds with the formula MnCl2(H2O)x, where the value of x can be 0, 2, or 4.
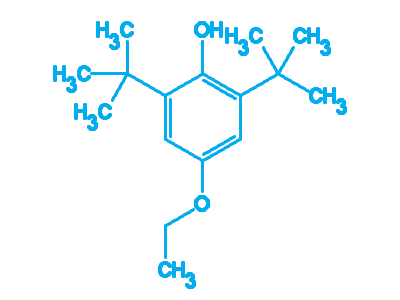
2-Ethoxy Phenol
CAS No: 94-71-3
2-Ethoxyphenol has been used as carbon and energy supplement in the growth medium of red-pigmented coryneform bacterium.

Manganese Chloride Tetra Hydrate
CAS No: 13446-34-9
Manganese Chloride Tetrahydrate is an excellent water soluble crystalline Manganese source for uses compatible with chlorides.